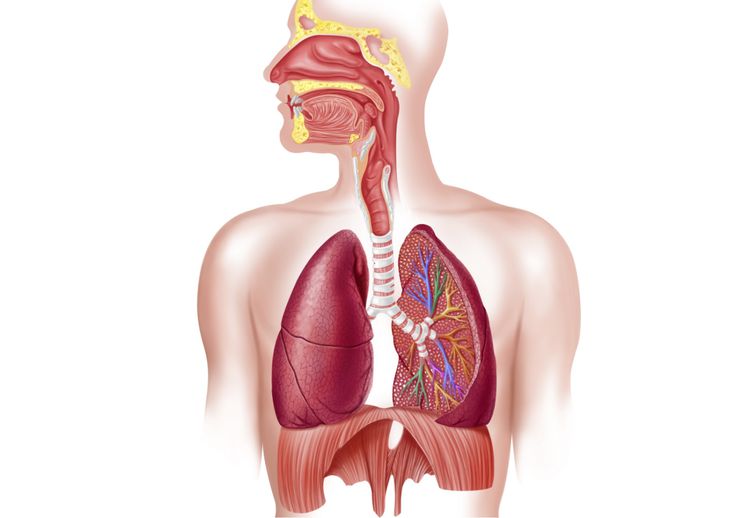
11. Respiratory System
All living cells must obtain oxygen and dispose of carbon dioxide. There are two different types of respiration, internal and external. Internal or cellular respiration is the exchange of gases between the tissue cells and their fluid environment. External respiration is the exchange of gases between the lung alveoli (singular - alveolus) and the external environment. This is accomplished by the respiratory system. The respiratory passages comprise the nose, larynx, trachea, and bronchi. The lungs are housed in the thoracic cage to which the respiratory muscles the intercostals, and the diaphragm are connected.
Transportation of respiratory gases Oxygen in a small amount remains in solution in the blood plasma. A large amount of oxygen enters into chemical combination with the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. Carbon dioxide also exists in small amounts in solution in plasma, mostly as bicarbonate, and a small amount is linked to the hemoglobin in red blood cells.