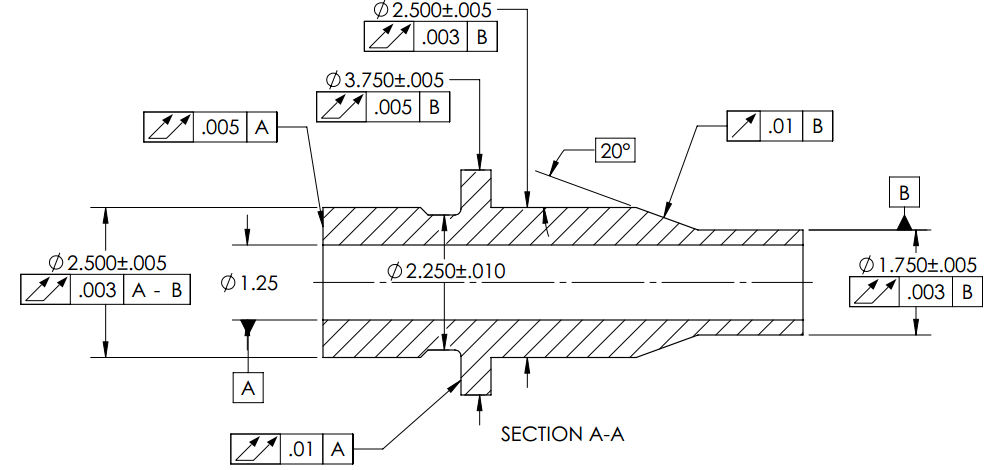
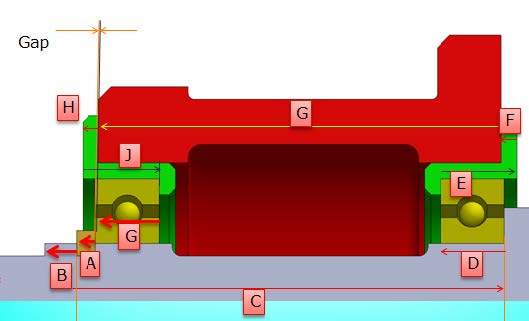
G4: Basic + Advance Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) + Tolerance Stack up Analysis
G4: Basic + Advance Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) + Tolerance Stack up Analysis
About the Class
Basics + Advance GD&T + Tolerance stack up
Basic + Advance Concept (16 Hours Approx)2.5 hours every day.
Weekday and well as weekend batches are available. Timing for weekday batches after office hours for professionals. Training will be on Microsoft teams and the link will be shared once enrollment completes.
Training will be live on Microsoft teams. And timing can be personalized. Batches start at the start of each month and complete within that month. Enrollment can be done till the last week of every month and the Schedule will be shared separately with members.
Each section involves the practice of calculation and application of geometric tolerances.
Course fee Includes 6 months of membership and Telephonic Personal consultation for any GDT and Tolerance Stack-up related issue.
Chapter 1- Engineering Drawing and GDT
- Engineering Drawings
- Introduction to Dimensioning
- Dimensioning Rules
- Co-Ordinate Dimensioning System
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing system Myths in GDT
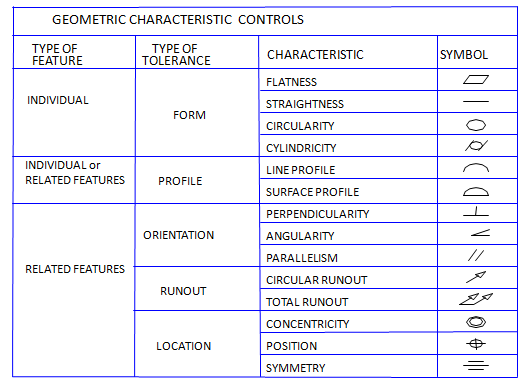
Chapter 2- Definitions and Symbols
- Definition
- Symbols
- Rules and Different concepts of GDT
- Limit of size
- Rule#1
- Rule#2
- Virtual condition
- Resultant Condition
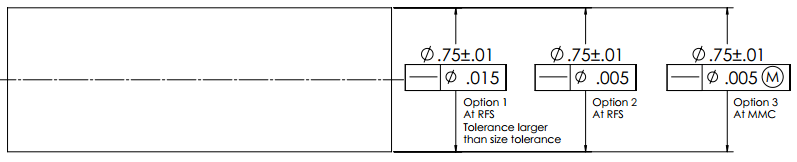
- Effect of RFS
- Effect of MMC
- Effect of LMC
- Bonus Tolerance
Chapter 3- Tolerance selection and Tolerance calculation
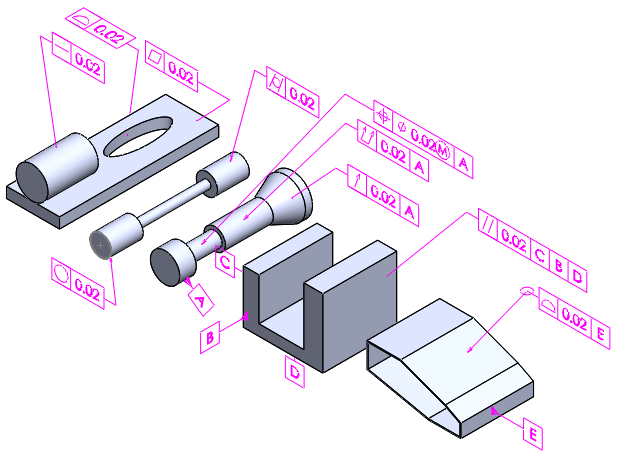
- How to select datum and particular geometric tolerance with a case study.
- How to calculate tolerance values or limits.
Chapter 4- Form tolerance
- How to select Form Tolerance
- Straightness tolerance
- Flatness tolerance
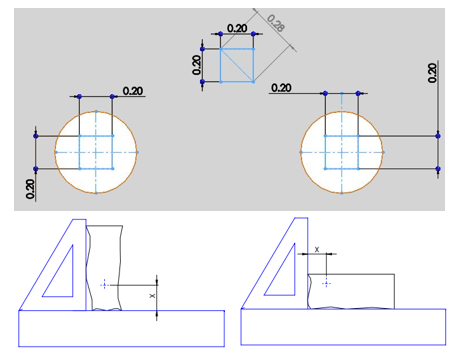
- Circularity
- Cylindricity tolerance
- Application over a limited length area
*Questions, Problems, and Solutions.
Chapter 5- Datum
- How to select Datum for Feature of Control
- Datum feature
- Datum identification
- Temporary Datum and permanent Datum
- Datum reference Frames
- Datum simulator
- Planar datum
- Datum feature of RMB
- Maximum Material boundary
- Least material boundary
- Datum shift
- Translation modifier
- Effects of shuffling datum in a feature control frame
- Datum targets
- The partial surface of Datum
- Rotational constraints due to axis
- Simultaneous requirement
- Identification
- Customized reference frame
*Questions, Problems, and Solutions.
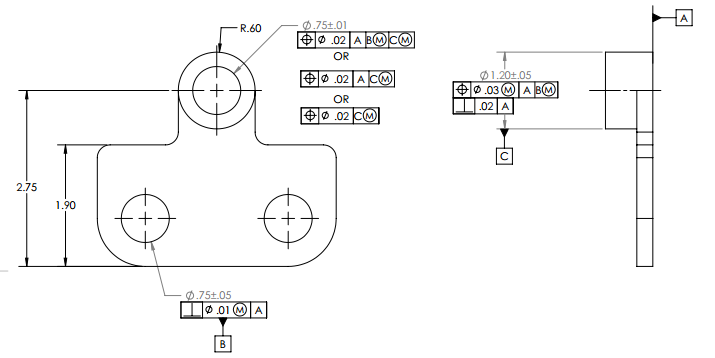
Chapter 6- Positional Tolerance
- How to select Location Tolerance
- Tolerance of location-positional tolerance
- Positional tolerance-RFS
- Positional tolerance -MMC
- Positional tolerance-LMC
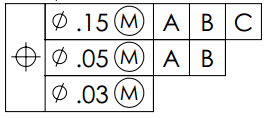
- Composite tolerance
- Multiple single-segment tolerance
- Application of projected tolerance zone
- Application of positional tolerance to counter bores different positional tolerance at end faces to non-circular features
- Coaxial control of pattern feature of size
- Simultaneous requirement
- Coaxial feature of size
- Positional coaxial control
- Concentricity
- Symmetrical relationship
- Controlling symmetrical relationships by position
- Symmetry tolerance
*Questions, Problems, and Solutions.
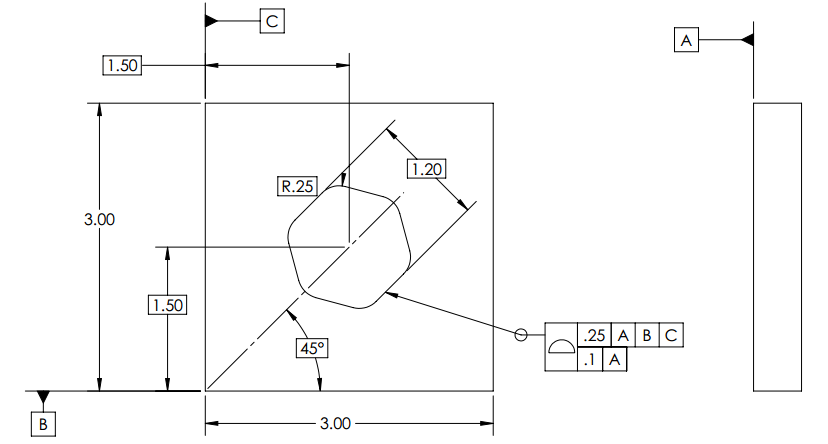
Chapter 7- Tolerance of profile
- How to select Profile tolerance
- Profile tolerance
- Uniform profile tolerance zone
- Bilateral tolerance
- Unilateral and unequal bilateral
- All around and all over symbols
- Different tolerance for different segments of cross-section
- Non-uniform tolerance zone
- CompositeTolerance application
- Composite tolerance application to single features
- Composite tolerance application for a feature in the pattern
- No datum is in the lower segment of the composite frame
- Primary datum A is repeated in the lower segment of the composite frame
- Primary and secondary Datum is repeated in the lower segment of the composite frame
- Individual feature control within features in the pattern
- Application of profile tolerance
*Questions, Problems, and Solutions.
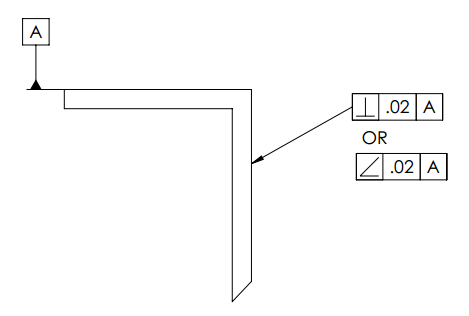
Chapter 8- Orientation tolerance
- Orientation tolerances
- Angularity
- Parallelism
- Perpendicularity
- Tolerance zone for orientation tolerance
- Orientation tolerance @MMC modifier
- Zero orientation Tolerances @MMC modifier
- Projected tolerance
*Questions, Problems, and Solutions.
Chapter 9- Runout tolerance
- How to select Runout tolerance
- Tolerance of Runout
- Datum section for Runout
- Circular runout
- Total runout
- Multiple Datum to control Runout control of datum surface
- The flat surface on the datum
- Application of circular runout on a curved surface
*Questions, Problems, and Solutions.
Summary of calculations
Question and Answer Session
Chapter 10 - Limit, Fit, and Tolerance
What, Why Limits- Fits and Tolerances Precision and Accuracy Various Fits
3. Tolerance Stack-up
Myths in Tolerance Stack-up.
What is tolerance Stack-up Analysis?
Why do a tolerance Stack-up Analysis?
Benefits tolerance Stack-up Analysis.
What are the driving factors in Stack-up analysis Assumptions and ways of doing stack-up?
Steps to be followed Rules.
preparing Loop diagram Converting all tolerancing systems to equal bilateral systems.
Examples Practice (Part Level and Assembly Level).
Fixed and Floating Formulas and Concepts.
Converting GDT; to Normal ± tolerance to use in stack-up analysis Few terminologies (VC, RC, OB and IB, Datum shift).
Form Tolerances – To include in Tolerance stack-up or not Orientation Tolerances on the surface and on the feature of size Profile (Composite tolerance effect as well) Positional Tolerance (Composite tolerance, when and how to include segments).
Datum shift assumption in Tolerance Stack-up Runout Consideration Symmetry and Concentricity Radial Tolerance Stack-up Part With Dimension and tolerance at an angle.
Statistical Tolerancing (RSS and MRSS)
Question and Answer Session
Requirements
You should have a basic understanding of Engineering drawing.